Stock market crash? No, but a rotation away from U.S. tech stocks is shaking up some investors
Social media to the contrary, the stock market remains far from “crash” territory, as anyone with a working memory of last March’s pandemic-inspired selloff, much less the global financial crisis of 2008, the dot-com bubble burst in 2000, or October 1987, would recall.
But a rotation away from the market’s recent leaders certainly does appear to be under way and volatile moves can be unsettling to some investors.
That could help explain why the term #stockmarketcrash was trending on Twitter Thursday, even though the Dow Jones Industrial Average DJIA,
The question investors should ask before tripping the alarm bells, however, is whether the price action is surprising or out of the ordinary, Brad McMillan, chief investment officer at Commonwealth Financial Network, told MarketWatch in a phone interview.
And the answer is no, given that a backup in bond yields, which seem to largely reflect increasingly upbeat economic expectations, look to be the main culprit, McMillan said.
While the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite COMP,
Thursday’s market weakness echoed the wobble seen last week. Both bouts of selling were sparked by a selloff in the Treasury bond market, which pushed up yields. The yield on the 10-year Treasury note TMUBMUSD10Y,
The Nasdaq was down more than 2% for the day, while the Dow, which fell more than 700 points at its session low, remained off around 320 points, or 1% on Thursday and the S&P 500 shed 1.2%. Those are sharp daily drops, but not extraordinary.
And it’s not unusual for stocks to begin pulling back as yields begin to rise, McMillan noted. It’s also not surprising that highflying growth stocks, which have seen valuations stretched in the post-pandemic rally, bear the brunt of the selling pressure.
Investors appear to be taking profits on those highfliers and using the proceeds to buy stocks of companies in sectors more sensitive to the economic cycle. The outsize weighting of tech- and tech-related shares in major indexes can leave them vulnerable to weakness as that process takes hold.
The price action of mega-technology and discretionary stocks — Apple Inc. AAPL,
“The weakness in large-cap tech has been weighing on the broad market averages sparking concerns of a market top and the end of the cycle. From our perspective breadth remains strong, a characteristic that is typically not present at market tops,” said Kevin Dempter, an analyst at Renaissance Macro Research, in a Thursday note.
Related: The stock market’s most sensitive sector says cycle isn’t anywhere close to turning
Small-cap discretionary stocks are at absolute highs, as well as multiyear highs relative to large-cap discretionary stocks, he said, which is a sign of broad-based participation. Trends are also strong for sectors, like energy and banks, that tend to be winners in higher-yield environments, while more economically sensitive groups like transports and services are also benefiting.
“Rather than a market top, we think this is rotational in nature with limited downside and going forward we want to be overweight high yield winners like banks and energy as there is likely further outperformance in these groups to come,” Dempter wrote.
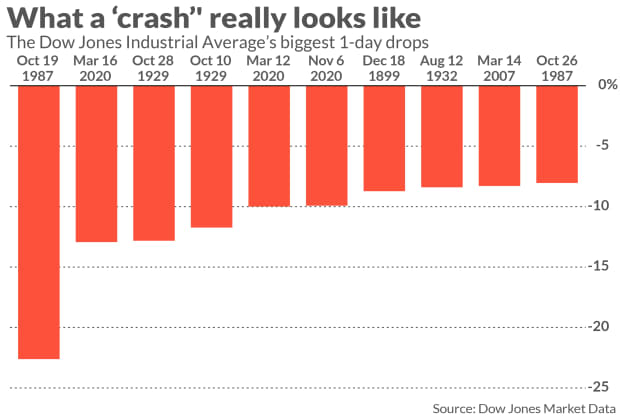
So what about that crash? The Dow continues to cling to a gain for 2021 and is less than 5% off its all-time high set last month, meaning that the most popularly followed stock-market gauge isn’t yet even in correction territory, typically defined as a fall of 10% from a recent peak. And it’s far from a bear market, which is defined as a 20% pullback.
Not all bear markets are the product of a crash — a more nebulous term, but one that implies a sudden and sharp fall. Some analysts define a crash as a one-day drop of 5% or more. Others see a typical crash as a sudden, sharp drop that takes the market into a bear market and beyond in a matter of a few sessions.
That was the case last year as it became apparent the COVID-19 pandemic would bring the U.S. and global economy to a near halt. The S&P 500 plunged from a record close on Feb. 19, dropping around 34% before bottoming on March 23.
Since those March lows, the S&P 500 remains up 71.2%, while the Nasdaq has rallied 68.9%. And even with its recent pullback, the Nasdaq remains up more than 90% over that stretch.




